Resource Leveling vs Resource Smoothing Techniques
In this post, we will show you the difference between Resource Leveling and Resource Smoothing in Project Management. They are the two most important Resource Optimization Techniques used in scheduling after resource allocation. We will see how resource constraints may impact the project deadline.
As we already know, when developing a new schedule for our projects we must follow a series of steps. First of all, we begin by establishing the procedures that we will use throughout the life of the project. Next, we will identify the list of activities and the logical sequence between them. Finally, in order to estimate the duration of these activities, we will need to evaluate resource allocation. For this, we need to know the type of resource to be used in every single case (labor, plant, machinery and/or material), as well as the number of units in each case.
But unfortunately, once we allocate resources to the activities of our schedule, we find histograms that show an overallocation of resources. In other words, we have a poorly optimized resource allocation. More resources are allocated than those our project is capable of absorbing. To help us sort this problem, there are two Resource Optimization Techniques:
- Resource Leveling
- Resource Smoothing
The PMPBok Guide defines these two techniques as follows:
Resource Leveling
What is Resource Leveling according to PMP? In this case, the Project Manager adjusts the start and finish of different activities in order to adjust the demand for resources per activity to the allowed limit. The Resource Leveling Technique can be used when we have resources in our project that: are shared among activities, are required in certain periods of time, have a restrictive use or there is overallocation of them. This adjustment may lead to an extension in the duration of the activity due to the restrictions it has in terms of the maximum number of allocated resources per period. Therefore, the use of Resource Leveling might modify the original Critical Path, expanding it in some cases.
Resource Smoothing
Let’s see what happens with Resource Smoothing according to PMP. In this Resource Optimization Technique, the Project Manager, in those activities that require it, adjusts the use of certain allocated resources in order not to exceed a previously defined limit of use. This limit could have been defined as a customer’s requirement, for issues related to Health and Safety, company policies or statutes. In this case, the Free Float of the activities that do not belong to the Critical Path is analyzed, and this is used to adjust the allocation of resources. In other words: Resource Smoothing technique does not increase the length of the Critical Path and may not be useful for the optimization of all resources.
Application of Resource Optimization Techniques
Let’s analyze all this on a simple Project Management example. Our project counts of 6 activities, whose durations and relationships are represented in Figure 01.
There are several resource constraints, represented in the Resource Histogram of Figure 01, that we must take into account:
(A) No period of time may have more than 5 resources assigned.
(B) No activity may have assigned more than 4 resources at the same time in a certain period of time.
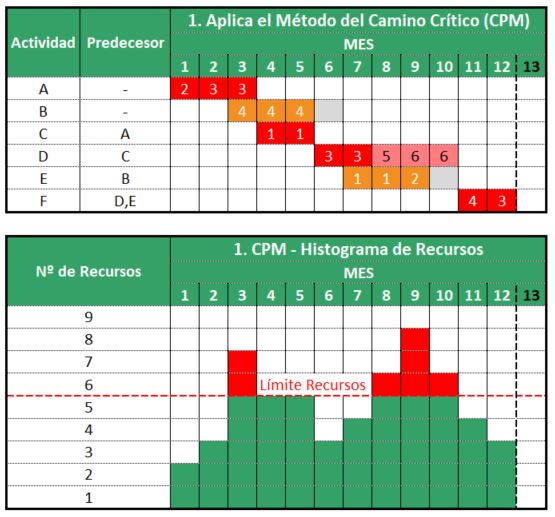
Next, we will apply the Resource Leveling and Resource Smoothing techniques in three steps:
Critical Path Method (CPM) application
First, we will analyze the program through the Critical Path Method (CPM). We observe that the activities A, C, D, and F determine the Critical Path of the project. Activities B and E have some float or slack, which is represented in gray. Months 3, 8, 9 and 10 require more than 4 resources, which is not allowed due to the first resource constraint (A). Activity D is using more than 4 resources for a few months, which is not allowed regarding the second resource constraint (B).
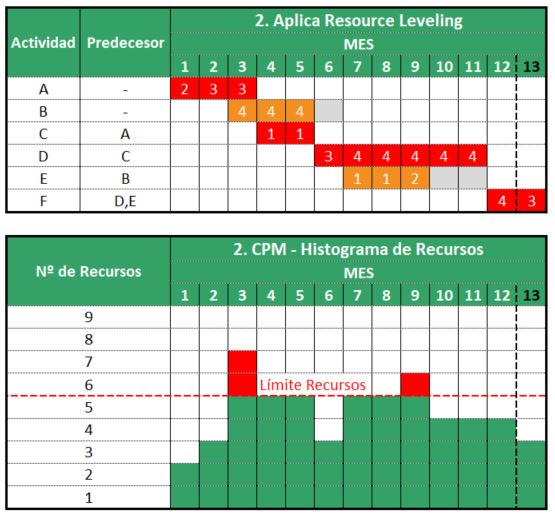
Resource Leveling application
Next, we will apply Resource Leveling to the Critical Path activities that fail the second restriction. This resource constraint refers to the maximum number of resources per activity and period. As we have seen, activity D is part of the critical path. Therefore, to reduce the allocation of resources by period to 4 it will be necessary to extend the duration of the activity. This will increase the duration of the Critical Path by a month. We can see this in Figure 2 and resource histogram below.
Resource Smoothing application
Finally, to fulfill the first restriction we will apply the Resource Smoothing to those activities with some float. In our case, activities B and E. In Figure 3 and resource histogram below we can see how our resource constrained schedule would finally be shown.
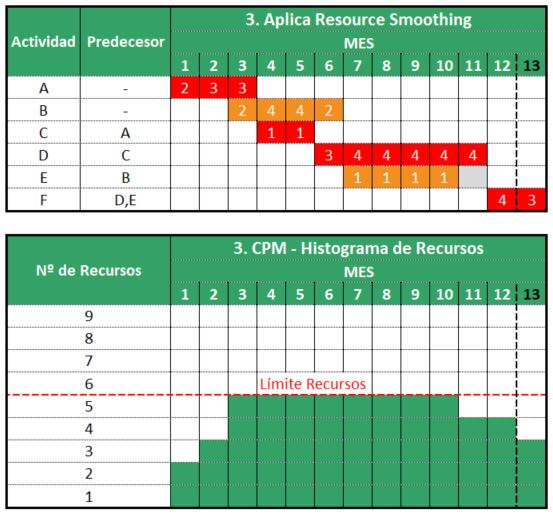
Once we have done these steps we will have a resource constrained schedule with optimized resources allocation. Both by activity and globally we have complied with all the constraints that were required.
IN PROJECT 2080 WE WOULD LIKE YOU TO REMEMBER
We have based the use of these two Resource Optimization Techniques in the application of the Critical Path Method (CPM). Next, apply Resouce Leveling first ensuring all activities comply with the resources constraints to be used per period of time. Finally, apply the Resource Smoothing ensuring you do not exceed the resource limit we can use per period of time. Remember to use both Resource Leveling and Resource Smoothing in Primavera P6 if trying to improve resource allocation in your schedule. If you are looking for a high level, efficient and optimized resource allocation schedule, adjust your project resource histogram thanks to Resource Leveling and Resource Smoothing techniques.




